Last Modified on January 7, 2025
Are you looking to learn Google Analytics 4 properly?
With a tool as complex as Google Analytics 4, it usually takes a while to familiarize yourself with all its features. In this guide, we’ll break down ten essential things you must master before calling yourself a GA4 expert.
We packed this guide with valuable insights, from understanding the new data model and calculated metrics to mastering custom metrics, dimensions, and the audience builder.
Don’t miss out on these crucial tips that will elevate your GA4 skills and help you make the most out of your data analysis.
Here are the ten things you need to learn Google Analytics 4:
- Measurement
- New Data Model
- Events & Conversions
- Enhanced Measurement
- Interface & Explorations
- Reporting Identity & Google Signals
- Attribution & Modelling
- BigQuery & Looker Studio Integration
- Audience Builder & Segmentation
- Measurement Protocol & API
Let’s dive in!
Measurement
How do you get the data from your website or mobile app into Google Analytics 4? Through measurement.
You install a tracking code to your website or app to see data flow into the tool.

There are various methods to install GA4 on your website, from manually digging through the code to using a plugin for your CMS.
Here is an opportunity to use tools like Google Tag Manager to send particular data to GA4 and manipulate it to suit your needs.
💡 Top Tip: Follow our guide to Install Google Analytics 4 with Google Tag Manager.
In GTM, you can create various Tags that you can use to send data to GA4.
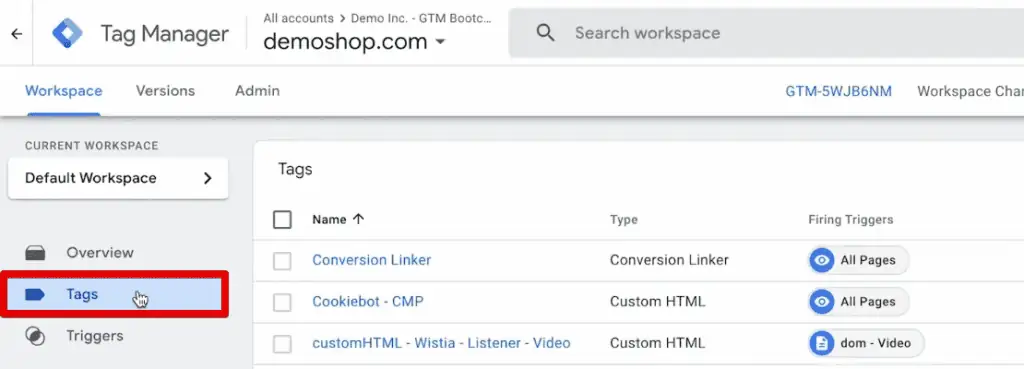
Then, you can create a GA4 event tag and send custom events with up to 25 event parameters per event.

That is the basis of true customization – only getting the relevant data your organization needs.
I encourage you to master the measurement part of the Google Analytics tool. You send the correct data into your tool so you can use it later on.
Something newly introduced in GA4 is the ability to track app and web data in one interface, which can be super powerful.
It is important and responsible to map out your tracking beforehand so you get usable data in your reports later.
New Data Model
The next thing to familiarize yourself with Google Analytics 4 is the new data model.
Understanding the data model is fundamental on your road to becoming an expert in GA4.
Understanding that everything revolves around an event will allow you to customize your installation and meet your client’s needs. Only those who can customize the tool to the business model can call themselves experts.
The ultimate way to customize your GA4 installation is to track custom data points with custom dimensions, custom metrics, and calculated metrics.
You can create these custom data points by going to the Custom Definitions section in the admin settings.

In GA4, we can create up to 50, 25, or 10 custom dimensions (depending on the scope they are), 50 custom metrics, and 5 calculated metrics for standard properties. Though limited, this number gives us a new level and room to customize our implementation.
You must understand how to utilize dimensions and metrics correctly to make your GA4 data better.
However, be careful with custom data in GA4. It is good practice to use and adhere to conventions on how to send data into the system so Google Analytics can interpret them.
Go ahead and read up on custom definitions and understand the data model behind them so that you can make your data better.
Events & Conversions
Events are the basic building block of GA4’s data.
Understanding the four different types of events that GA4 can receive and how it interprets them is vital for your reporting needs later. We have automatically collected events, enhanced measurement events, recommended events, and custom events.
💡 Top Tip: Here is a guide to get you started – How to Track Events with Google Analytics 4 and Google Tag Manager.
Don’t skip on a solid foundation of naming your events correctly and choosing the correct event parameters to ensure you can use your data in the reports later. All of this can make or break your data points later on.
Once the data is in the system, you should set up conversions. You can easily set an event as a conversion by going to the admin settings.
Here, go to data display → Events. Beside the event name, click on the toggle in the Mark as conversion column. A prompt will pop up at the lower-left corner to indicate the successful marking of the event as a conversion.

This new flow of marking a conversion inside GA4 is easy to understand. However, people sometimes miss certain parts because they need to dissect certain events and only count certain parts of the event towards the conversion goals.
💡 Top Tip: Check out our guide on How to Set Up GA4 Conversion Tracking, where we discuss three more customized ways of setting up conversions.
Ensure you understand which events you want to mark as conversions and follow the appropriate steps for setting them up.
Enhanced Measurement
An essential topic you should understand to learn GA4 is enhanced measurement events.
One of the surprising additions to GA4 has been enhanced measurements or the so-called GA4 auto-tracking functionality.
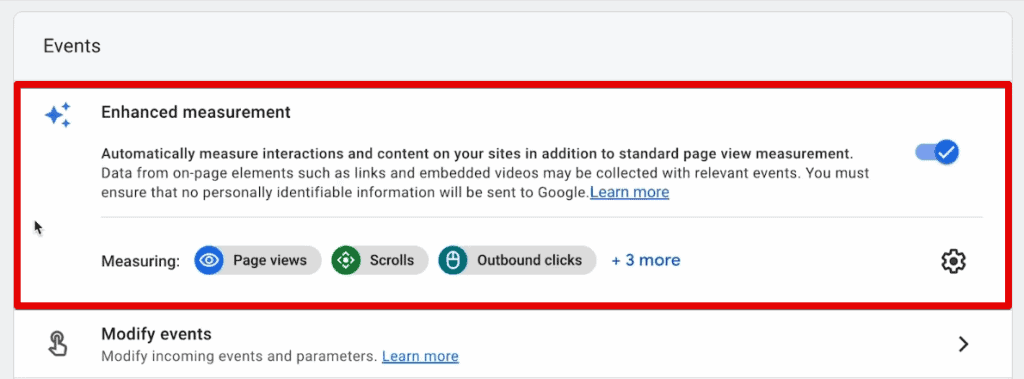
Google tracks a number of events by default once you enable this tracking. These events include scrolls, outbound clicks, site searches, video engagements, file downloads, and form interactions.
It is fantastic news for anyone who doesn’t want to spend time customizing their installation and is okay with the standard data that flows into the account.
For those who want to turn pro, you need to know how Google tracks these events. Understand when these enhanced measurement events fall flat and what problems they might bring into your account if the data does not show as expected.
Not all forms of tracking measure equally, and this enhanced measurement functionality can often break.
It is well worth knowing how to set up these events manually in Google Tag Manager for your tracking to be solid and for you to be able to understand and debug it later.
If you choose to track these events manually, ensure that you toggle this setting off or for just the individual events you set up customized tracking.

Interface & Explorations
Once you have it in your system, finding the relevant data in GA4 might not be hard for you right now. However, you can boost your GA4 skills by using all the different features to wrangle your data around.
You can build custom reports to ensure you get to your desired insights or dive into making custom insights. From filters, comparisons, and adding custom reports to the library, there are many ways to get efficient within the GA4 reporting section.
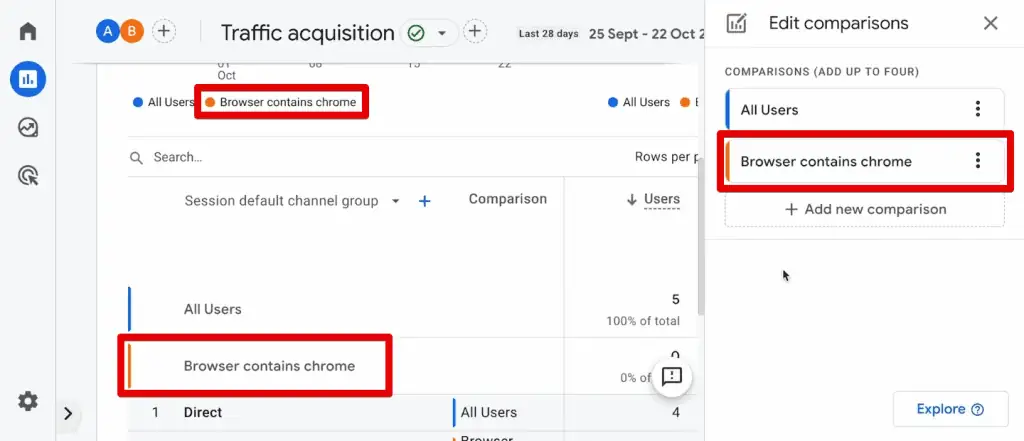
Let’s demonstrate one of these features in the traffic acquisition report.

Click Add Comparison.

Once you add a comparison item, notice a new data point in the charts and tables on the page, represented in a different color.
Next, there is a whole different reporting module with explorations.

You need to know your data fully to put it together from scratch in the exploration section. Then, it can be a powerful tool to help you build the report you envision with all its different visualization forms and funnel building.
💡 Top Tip: If you’re looking into creating custom funnels, check out our guide on How to Create a Funnel Exploration Report in GA4.
You must spend hours with the explorations section before you can call yourself a master of GA4.
Reporting Identity & Google Signals
Additional features to include in your journey to learn Google Analytics 4 are the reporting identity and Google Signals.
Now, how does GA4 identify a user? In the past, the answer would be mainly cookies. However, using cookies is not always possible with the growing privacy restrictions.
That is why GA4 introduced some new methods to help us fill the gaps in our data. You can identify your users with the following identity spaces: the user ID, Google Signals, device ID, and modeled data.

You can combine cookie data with all four identity spaces with the default Blended reporting identity. Other options are Observed, where you only use the user ID, Google Signals, and device ID, and Device-based, where you only use the device ID.
You can control the reporting identity GA4 will use in the admin section.
Knowing about these different ID methods is vital for understanding your data and how it can affect your reporting. For instance, Google Signals can be a mess with the data that applies to it, and thresholding might occur.
Unfortunately, it is necessary to install Google Signals to use Google Ads effectively with the GA4 reporting capabilities. The question is, are you willing to make this trade-off? Do you understand the implications of this trade-off?
💡 Top Tip: If you accept this trade-off, check out Google’s documentation on activating Google Signals for GA4 properties.
Knowing about these different reporting identities, how to implement them, how to use them effectively, and how they impact your data is vital when learning Google Analytics 4.
Attribution & Modelling
Attribution is about determining which marketing channel gets credit for a particular conversion. GA4 offers automatic attribution with a preferred model, but that doesn’t make things easier.
For instance, only some reports use the same attribution model, and you need to get used to the quirks and the different attributions out there.
To select the attribution model, go to Admin → Attribution settings.

Additionally, look into the different understanding of sessions in GA4 and how it impacts your attribution.
Charles Farina has a great blog post discussing this topic, all the quirks, and how you cannot trust attribution fully yet in GA4. Hopefully, Google will fix these soon.
Another complication is the new modeling features that are going on in the background.
If you use consent mode in combination with GA4, Google might model your data. It will automatically fill in the missing data based on the data you previously sent into the system and their machine learning algorithms.
It is a fascinating feature because you might be missing data based on the privacy features you have installed on your website or any tracking preventions that might be going on.
At the same time, it is a little bit of a black box. It is trial and error to determine which data Google modeled and how it impacts your data.
So, keep an eye out for any modeling going on in your account.
BigQuery & Looker Studio Integration
To learn Google Analytics 4, you must also look into BigQuery and Looker Studio integrations.
It is a fact that GA4 does not pretend to do everything in the analytics world. Reporting and dashboarding, for instance, are not particularly good in GA4, so Google offers a free connection to Looker Studio.

With this tool, you can pull in data from GA4 and create your reports and dashboards on the fly in this interface. It is handy when you need to present your data and show it to your clients.
The best thing about this tool is that your clients are not required to log in to GA4 because you can share the report without giving them access to the data source.
If you want to take it a step further and follow what professionals do, use the BigQuery connector because GA4 can connect directly to the warehousing solution of Google, BigQuery.
With this connection, we can get all our raw data out of the system and use it however we want, like analyzing data with the attribution model you want.
For example, you can combine your GA4 data with your CRM data or export it to another tool that does a better job of analyzing that data than GA4. For BigQuery, you need a little learning in SQL to get things working and output the data you want.
💡 Top Tip: We have a BigQuery Tutorial to help you determine what BigQuery is all about. Check out our guide on the GA4 SQL Tool for BigQuery, a handy site that writes SQL codes for you.
Suffice it to say that Looker Studio and BigQuery are something you should look into if you haven’t yet.
Audience Builder & Segmentation
Analysis in GA4 is all about filtering down your data and getting to that end set. The most powerful way of filtering your dataset is through segments and the audience builder.
The new possibilities of the audience builder let you dig into the data like never before because you can use insights like sequences and implement time. You need to have a good understanding of the data itself and how it is put together.

A fundamental piece to understand is what the scope is all about and which parts of your data a dimension is assigned to. It is crucial to understand that part so you can use your segments effectively. Otherwise, you might get garbage out when building your report.

Additionally, the audience builder has a new feature of audience triggers, which build membership groups you can assign users to and deploy an event, which you can then turn into a conversion.

Audience triggers are a fascinating feature, but they also make it harder to debug later and know where events are coming from.
💡 Top Tip: Check out our article on the Top 5 Benefits of GA4 for PPC Specialists to find a dedicated section where we explain audience triggers in more detail.
The audience builder is a standard feature in GA4, but it takes a lot of practice to master it.
Measurement Protocol & API
The tracking code is not the only way to send data into GA4. You can also use the measurement protocol, which is GA4’s API, so to speak.
With this endpoint, you can connect GA4 to anything from the Shopify backend to your point of sale system, your stripe, and so on, essentially any software that can connect to an API. You would probably use it with your developer to make that connection work.
There is a learning curve involved because you need to get the request right to show the data correctly in the system later. You must create an API secret to send additional events through the measurement protocol.

Next, you can use the GA4 event builder to validate if it works correctly and create the event payload.

Getting away from just the tracking code is a fascinating feature inside GA4, and Google made it even better with this version.
Quirks & Shortcomings
Before you go, there is one bonus that I need to mention, and it is mastering the quirks and shortcomings of GA4.
GA4 isn’t perfect. The biggest challenge over the past few months is dealing with the shortcomings, which might or might not be fixed soon.
It can be frustrating working with the tool, finding inconsistencies, having data changes, and realizing that certain things are not behaving as they should.
If you’re already on your way to mastering this tool, then you must learn to live with these uncertainties. Maybe we should all embrace the quirks of this tool right now.
Summary
There are many resources you can choose to learn Google Analytics 4 and stay up to date on what other workarounds other people come up with to validate if the data is correct.
Maybe there is something wrong with your implementation, or there is a shortcoming of the tool.
It takes a lot of time, digging into the forms, and knowing and reading up on the latest developments in the industry. There are many different resources, and I hope we are one of these sources for you in the future.
If you want to dive deeper into the features of GA4 without altering your data, consider using the GA4 demo account. It can be a fantastic resource for those just starting but know that there will be some limitations.
What do you think of our list? Are there any other features we should have included here? Let us know in the comments below!