Last Modified on January 11, 2024
Google Tag Manager vs Global Site Tag: what are they, and which should you use?
Google Tag Manager and the Global Site Tag can seem interchangeable, but they are two different tools and should be chosen wisely based on your needs.

Sign up to the FREE GTM for Beginners Course...
In this side-by-side guide, we’ll learn about the Global Site Tag, Google Tag Manager, their similarities and differences, and what you can do with them.
If you haven’t installed GTM already, check out our handy guide on how to install GTM to your WordPress website.
An overview of what we’ll cover:
- What is the Global Site Tag?
- What is Google Tag Manager?
- The difference between the Global Site Tag and Google Tag Manager
- When should you use the Global Site Tag vs Google Tag Manager?
- Which one do we recommend?
- Frequently asked questions
So let’s dive in!
What Is the Global Site Tag?
The Global Site Tag is a tracking code that you install in the header section of your website. It tracks information on your website and forwards it to Google Analytics or other Google-associated tools.
Let’s see how to access this code in our Google Analytics account. On the homepage, click on Admin → Tracking Info → Tracking Code.

Google introduced this all-in-one code in 2017. Before that, each marketing product had its own tracking code. This meant that to use Google Ads, you needed to add the conversion.js code or analytics.js for Google Analytics.
Every tool required a separate installation of code. As a result, every new addition of code would increase the complexity of your site’s HTML and JavaScript execution.
And what if you just wanted to see pageviews on your website? You would have to send this data to different tools and consolidate it, which is a bit of a pain.
Thus, this implementation became quite inefficient.
To solve this problem, Google came up with a more holistic solution for your tracking requirements. With the Global Site Tag (gtag.js), most of the work was cut out for the user—and you only had to install the code once.
Let’s demonstrate how this works.
How Does It Work?
All you have to do to install this code is add the script to the head section of your website. The Global Site Tag will be on the top of all the tracking scripts. Below it, you can configure any other tools like Google Analytics or Google Ads.

These tools are added to the background automatically. So when you send your data for analysis, the codes don’t need to run multiple times.
This also reduces the base code length and increases the efficiency of the data.
What Is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a tag management system that acts as a common tool for running all different tracking tags, just like Global Site Tag.
The key difference is that, unlike Global Site Tag, Google Tag Manager is not confined to Google tracking tools. Google Tag Manager accommodates a variety of other tools, including templates from community members.
You can manage not only Google Ads and Google Analytics, but many other tracking Tags like Facebook Pixel or LinkedIn Tag through the single central interface of Google Tag Manager.
Let’s see how this works!
How Does It Work?
Working with Google Tag Manager is quite easy.
You can deploy all your tracking Tags such as quotes from Google Analytics or Google Ads through its central interface. You can also put your Facebook Pixel into a custom HTML Tag and deploy it on Google Tag Manager.
In fact, you can do much more with Google Tag Manager than with the Global Site Tag. For example, you can test a code before deploying it, show a graphical user interface, control multiple versions, and access different triggers that you can utilize to deploy all this tracking.

However, the premise remains the same. Just like the gtag.js implementation, you can define a single interaction with a trigger that you want to track, then send data to different tools.
So let’s compare them further to get a better understanding.
What is the Difference Between the Global Site Tag and Google Tag Manager?
We already know that both the tools are similar in the way that they can deploy either multiple tracking points or one tracking point to a variety of Google tools.
In simpler words, if you want to send tracking information to your Google Ads or Google Analytics account, you easily accomplish this with either Google Tag Manager or the Global Site Tag.
But how are these tools different from one another?
There are three main differences between Global Site Tag and Google Tag Manager: third-party tool compatibility, additional functionalities, and graphical user interfaces.
Third-Party Marketing Tool Compatibility
The first and major difference is the compatibility of Google Tag Manager with other tracking tools.
While the gtag.js script only works with Google tools, Google Tag Manager allows you to send data to any tool that has a JavaScript-based tracking code.
Even if Google Tag Manager doesn’t have a native integration with your favorite tools, you can usually install tracking codes via a Tag template or a custom HTML Tag. It is thus more flexible in that regard and agnostic to any tracking tools.

Functionality
The next major difference is the functionalities that the two provide.
The Global Site Tag doesn’t add any bells and whistles to your tracking system. What you see in your Google tools (Analytics, Ads, etc.) is exactly what you get.
Google Tag Manager provides more features in its interface. You can update new versions of your tracking implementation or revert to an old one if you find bugs. You can also test and debug your implementation using GTM’s Preview Mode to keep each version as clean as possible.

User Interface
Lastly, Google Tag Manager has a graphical user interface that is not available for the Global Site Tag.
This means that with the gtag.js, you’ll need to do all your site’s tracking coding on your own. The Global Site Tag is effectively invisible to you as a marketer or developer except for in the website’s script. This will require at least a basic knowledge of JavaScript to configure your tools correctly with the Global Site Tag.
Hence, it becomes difficult to install some advanced functionality such as button click tracking on the Global Site Tag.
Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, has a very intuitive and user-friendly interface that requires little to no JavaScript knowledge (unless you’re building your own custom HTML Tags).

It’s much more approachable for marketers who don’t pull double-duty as developers.
Differences
| Global Site Tag | Google Tag Manager |
| Compatible only with Google marketing tools | Compatible with all 3rd-party marketing tools |
| Simplified implementation with more limited functionality | Provides functionalities like testing of codes, version control, etc. |
| No graphical interface; JavaScript installation required for advanced tracking | User-friendly, graphical interface that supports advanced functionalities |
When Should You Use the Global Site Tag vs Google Tag Manager?
The Global Site Tag is just a mini version of Google Tag Manager. Based on your tracking requirements, you can choose when to use each tool.
For example, if you have a new website in which you want to set up a tool to track your visitor behaviour, you’ll need to install Google Analytics. This can be done by both Global Site Tag as well as Google Tag Manager.
Global Site Tag
To install Google Analytics on your website with the Global Site Tag, you will be asked to add the gtag.js code in the head section.
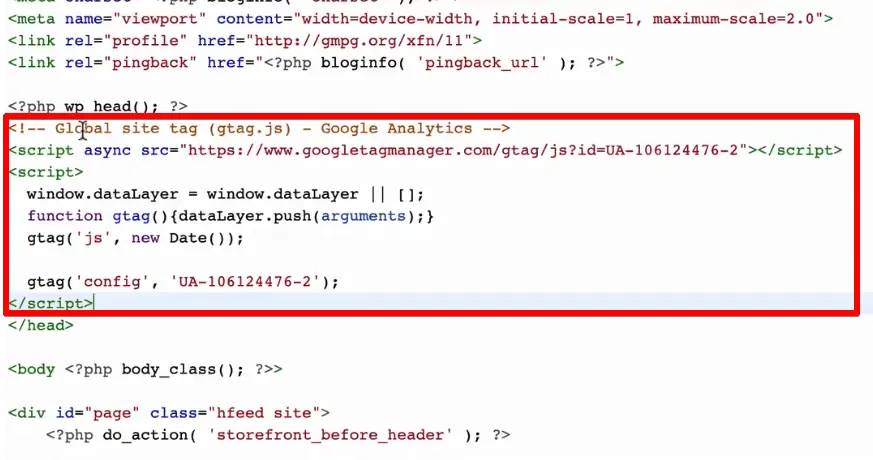
Going further, if you want to drive more traffic to your website, you can choose to add Google Ads as well. This can be easily done since we already installed Global Site Tag earlier.
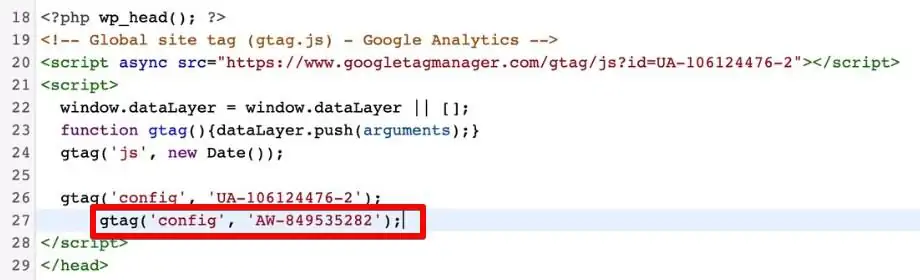
The Global Site Tag will then send over data to both Google Analytics and Google Ads.
However, if you wish to expand your website tracking even further by using the Facebook Pixel, Microsoft Advertising (formerly Bing Ads), or LinkedIn advertising, then the Global Site Tag won’t support your needs.
If you keep on adding different codes to your website, it will start creating chaos inside the HTML. It will become difficult to track which code fires which tool—a developer’s nightmare when you finally decide to clean it up later.
Google Tag Manager
At this stage, the wise option will be to choose Google Tag Manager. This will decrease your workload significantly and also increase efficiency.
Google Tag Manager will give you a graphical user interface that makes it easier to manage multiple codes.
Hence, it might be a better option to use Google Tag Manager instead of adding codes manually to your page.
Which One Do I Recommend?
If given a choice, I’d definitely recommend using Google Tag Manager, even to marketers who are capable of adding the manual codes.
Similarly, if you have a new website and want to install just one tracking system on it, Google Tag Manager will still be a preferable choice.
It’s always better to have your website processed by a Tag management system rather than adding the codes manually.
However, for legacy cases, it might be time-consuming to replace all the old codes with Google Tag Manager, so it would be better to continue using Global Site Tag.
Also, if you feel that you want to do the tracking manually and if you already have some modules, you could use the Global Site Tag.
But for most other cases, I would recommend using Google Tag Manager as it is a widely accepted tracking system in today’s world.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Install the Global Site Tag through Google Tag Manager?
In a way, yes, you can sort of install the Global Site Tag through Google Tag Manager.
One thing to remember here is that the Global Site Tag is a mini version of Google Tag Manager itself.
So it’s already sending data over to different tracking tools. This means you will not install the Global Site Tag into Google Tag Manager per se, but take these tools and install them into Google Tag Manager.
So if you’re sending data over to AdWords or to Google Analytics via the Global Site Tag, then you would need to utilize the Tag template within Google Tag Manager to deploy the same tracking points with Google Tag Manager.
🚨 Note: Do not take the gtag.js script and put it into a custom HTML Tag of Google Tag Manager. That is not a best practice and would lead to problems in your tracking.
Is It Ok to Have Google Tag Manager and Global Site Tag Installed on the Same Page?
Technically, yes. Google Tag Manager and Global Site Tag are compatible with each other and can be installed on the same page.
However, both these tools utilize some common resources that can lead to conflict in some cases. For example, the data layer is one such resource that is used by both tools.
Therefore, it is important to be careful while adding both of them together. You will also need to test the implementation of tools by checking whether the correct data is sent to these tools.
Overall, the process is doable but complicated. That’s why I would recommend not to install them together on the same page.
🚨 Note: For individual tools, you should use either Google Tag Manager or the Global Site Tag, but not both. If you install both of them, you will end up sending duplicate data to any tools that are connected to your website via both implementations. This could result in double-counting pageviews and other metrics, which will obviously ruin your data.
What are the main differences between the Global Site Tag and Google Tag Manager?
The main differences between the Global Site Tag and Google Tag Manager are:
1. Third-Party Marketing Tool Compatibility: Google Tag Manager is compatible with all third-party marketing tools that have JavaScript-based tracking code, while the Global Site Tag is only compatible with Google marketing tools.
2. Functionality: Google Tag Manager provides additional functionalities like testing codes, version control, and debugging, whereas the Global Site Tag offers a more simplified implementation.
3. User Interface: Google Tag Manager has a user-friendly graphical interface, making it easier to manage tracking codes, while the Global Site Tag requires JavaScript knowledge for advanced tracking configurations.
When should I use the Global Site Tag vs Google Tag Manager?
You should use the Global Site Tag when you only need to track data for Google marketing tools like Google Analytics and Google Ads. If you require compatibility with third-party marketing tools or additional functionalities like testing and version control, it’s recommended to use Google Tag Manager.
Is it okay to have Google Tag Manager and the Global Site Tag installed on the same page?
While it is technically possible to install both Google Tag Manager and the Global Site Tag on the same page, it can lead to conflicts and complications due to their shared resources. It’s recommended to use either Google Tag Manager or the Global Site Tag for individual tools to avoid sending duplicate data and ensure accurate tracking.
Summary
In conclusion, we can say that Google Tag Manager wins between the two—Google Tag Manager vs Global Site Tag.
Global Site Tag is a mini segment of Google Tag Manager. It is neither as flexible nor as powerful as Google Tag Manager. For some specific use cases, it can be the right choice. However, for most tracking requirements, you should install Google Tag Manager.
If you are new to Google Tag Manager and want to learn its basics, check out our in-depth Google Tag Manager tutorial.
Which one do you prefer between Google Tag Manager and Global Site Tag? Have you installed the Global Site Tag through Google Tag Manager? Let us know in the comments below!





I was looking for this explanation for a while and I could not find. Thanks for it. 🙂
Glad it was a useful guide for you!
Thank you so much – very helpful. Thank you for clarifying that if you use GTM, the global site tag is basically not necessary, and in fact, it could cause problems when they are used together. I wish Google would combine a lot of their services/tools. Analytics, Search Console, Tag Manager, gtag.js…. it’s a lot to keep track of, esp. when you have a different container ID for each tool.
What if we already have gtag.js installed on the site and now I want to upgrade to GTM. What is the procedure for that. Can we do that without any compromise on the data that we already have?
Also, can both codes be placed on the same website without any misleading data being fired to Analytics? Help!
first I would decide wether you want to use GTM or Gtag. I would not run both on the site simultaneously, simply because it can lead to conflicts and is harder to debug.
In order to migrate I would:
1. take stock of what fires, where, when with the gtag (make a tag plan)
2. install GTM and prepare all your tags inside of it. Test everything in the preview mode
3. Remove all your gtags and submit your version so it goes live.
This will result in no data loss.
How do I remove the Global Site Tag if I’m using GTM? For additional context, I have a wordpress site and I use elementor .
how did you install it? Just reverse that step
Thanks for the explanation. Helped me to get the basics of these two systems.
I have some dynamic remarketing codes installed with gtag on my page. I think if i delete gtag config code on my webpage and move to gtm, my dynamic remarketing codes which use gtag parameters will not work. How can i handle with it 🙁
var FBurunler = new Array();
var remarketingProducts = new Array();
[loop_product]
remarketingProducts.push(“{productId}”);
FBurunler.push(“{productId}”);
[/loop_product]
gtag(‘event’, ‘page_view’, {
‘send_to’: ‘AW-xxxxxxxx’,
‘ecomm_pagetype’: ‘purchase’,
‘ecomm_prodid’: remarketingProducts,
‘ecomm_totalvalue’: {total}
});
<!– Dinamik Remarketing Kodu —
Thanks, Julian! Very helpful
Hello,
I placed Google Analytics code in head section of my website but don’t know it is placed correctly or not. Google Analytics showing error “not getting hits”, Can you please tell me how can I check that.
Thanks.
Hi Mukesh! I have checked your webpage, and I can see Google Analytics running there. You could check it with the extension that is called Google Tag Assistant or verify your implementation with the help of the Analytics real-time report. Can you see any data flowing there?
I moved everything over to GTM and got rid of the global site tag. However, in tag assistant in GTM the AW-xxxxx container is now missing, and its no longer possible to debug its output. If I add back the global site tag with config=AW-xxxxx the container is present again in the GTM debug console. I tried setting AW-xxxx up the GA4 additional products in the data stream, no luck. GTM has all the individual GAds conversions, linker, remarking tags etc, but still no AW-xxxxx container shows up in GTM debug unless I define it through the global site tag… Read more »
Hey Ben, if you are using GTM, you should not have a gtag implemented at the same time, as this would cause double tagging. GTM is deploying that automatically when you set up an Ads conversion.
Google Ads Conversion tracking now doesn’t give an option to use Google Tag Manager. When attempting to add Google Ads Conversion tag in GTM it asks for Label, which is nowhere to be found in Ads interface anymore.
So the $1000000 question is – how do you implement ads conversions with GTM?
Hey there, Mark! You should click New conversion action. Then the system will ask you to enter the URL. After your domain is scanned, you would have to scroll down and select the option Add a conversion manually. When everything is set up, you will see the GTM implementation option. Here’s the video guide for you: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S5oVy4XKpG8&t=0s
I have the same problem. I just see the options ‘Edit your website code’ & ‘Email instructions to your webmaster’ The Tag Manager option is simply not visible in the gAds interface? 🤔
Yes, there was a Google Ads update, and the new interface is not very intuitive indeed. Please check the video I posted above and let me know if you managed to set it up.
Works :+1: Thanks
I have a WordPress plugin called Beehive Pro. It allows me to add the GA4 tracking id and a GTM code. In GA4, the enhanced measurement for form submission data is very off, and I want to set up that as a custom event in GTM. I however, don’t want to stop using the other enhanced measurement tools such as the site search, etc. Can I do this if I am not collecting duplicated data? How can I ensure I am not collecting duplicate data?
Hey Kelsie! Yes, we also track our form submissions manually, since the Enhanced Measurement tracks many false positives, which causes too much noise in the data. You should go to your GA4 Data Stream and click on a wheel under Enhanced Measurement (Configure Enhanced Measurement). This is where you can have granular control over your Enhanced Measurement settings. If you want to set up a custom event via GTM, you should simply deactivate Form Interactions there to avoid duplication.
Hi Sofia, Thanks for the response! I have deactivated the form submissions, but my main concern is having the GTM and gtag running on the site simultaneously. Since I want to have the other enhanced measurements on, but also track my custom form event through GTM do I need both tracking or can I just have GTM? Or am I misunderstanding this.
I have a website that uses a React app for parts of the web site. So far I’m sending custom events to GA3 using ga.send(xxx). Now I’m trying to migrate these events to GA4, but I’m struggling a bit. If I push this event data to the data layer, do i really need to setup every single event in GTM and define all the dlv’s? This seems like an insane amount of busy work when I can just just gtag to send the events straight to GA4 ( gtag(“event”, properties); ) However, it doesn’t seem easy to use gtag when… Read more »