Last Modified on December 16, 2024
We have trained numerous students over the years here at MeasureSchool.com. In this post, I have compiled the absolute top 10 Google Tag Manager skills I think marketers should focus on to become Google Tag Manager experts.
There are many great resources to address particular features in GTM, but this time we are going to dive into some basics.
Knowing what to look for, what to fix, and ultimately where to get help is key to acquiring Tag Manager skills.
Here are the 10 Google Tag Manager skills you should know:
- Planning
- Setup
- Workflow
- GTM Components
- GTM Data Layer
- GTM Events
- HTML/CSS/JavaScript
- Advantages/Shortcomings of GTM
- Debugging
- Where to Get Help
If you’re new to Google Tag Manager, make sure to check out our handy Google Tag Manager tutorial.
1. Planning
Of all the Google Tag Manager skills you need, this one is for sure the most important.
Before you start doing anything, you’ll need to have a solid understanding of what you want to track and be able to plan out exactly what needs to be done.
Especially for broader implementations, you should plan out your progress and start inputting tags, triggers, and variables step by step and never all at once. (This also limits the possibility of messing things up.)
Check out our post on our planning tag deployment process if you want to find out more.
Note: We’ve updated our previous tag planning template, and you can access the new version here. You can find the demo for multiple use cases making it easy for you to start right away!
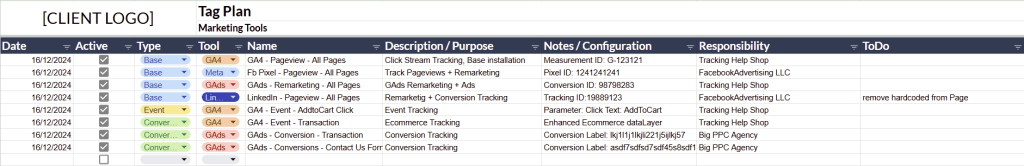
2. Setup
Google Tag Manager is not useful if it’s not correctly installed and configured. You need to be able to make sure it is working flawlessly on all pages and be able to debug problems.
Also, the account setup itself requires special attention to organize future needs with the Workspace, Environment, and User Management.
3. Workflow
Having an established workflow lets you implement your tags fast, more efficiently, and most importantly, consistently.
Many best practices have evolved over the last years, but one stands out: having a naming convention for your tags, triggers, and variables. Also, writing a description with the main consequences before publishing tags and triggers can be a lifesaver.
Alright, in the first 3 concepts we covered some preparations – now let’s dive into the ideas you need to know to master GTM.
4. GTM Components
Google Tag Manager consists of Tags, Triggers, Variables, and of course the DataLayer. These components are interconnected and can’t exist separately.
Having a solid understanding of these components and how to connect is essential. Especially if you run into trouble, you need to know how to check each part and make sure they are working as expected.
So better learn about the GTM components if you are not confident in their function yet. This leads us to the next essential concept you need to master.
Let’s dive into each component a bit further:
- Tags: Snippets of code that send data to third-party systems like Google Analytics or Google Ads.
- Triggers: Define the conditions under which tags should execute, such as page views or button clicks.
- Variables: Placeholders that store values to be used in tags and triggers, like product names or prices.
- DataLayer: A structured object that holds information for GTM to use in tags, triggers, and variables.
5. GTM DataLayer
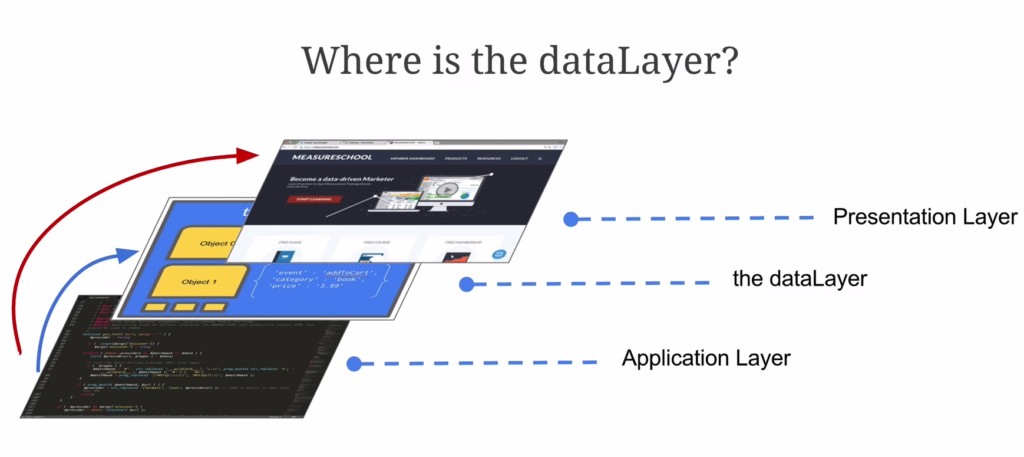
The Data Layer in Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a structured JavaScript object that serves as a central repository for storing and passing data between your website and GTM. It acts as an intermediary layer, allowing your website to communicate key information (e.g., user actions, page details, or e-commerce transaction data) to GTM for use in tags, triggers, and variables.
Key Characteristics of the Data Layer:
- Centralized Data Handling:
- The Data Layer consolidates all the data you want to track in a single place, making it easier for GTM to access and process it.
- Flexibility:
- It allows for custom event tracking, user-defined variables, and advanced use cases like e-commerce tracking.
- Event-Driven:
- You can push events into the Data Layer (e.g., form submissions, button clicks) to trigger specific GTM actions.
Why the Data Layer is Useful:
- Decouples Data from Website Code:
- By separating tracking data from website code, the Data Layer simplifies tag management and reduces dependencies on developers.
- Improves Accuracy:
- Provides a standardized way to track events and pass data, reducing errors in analytics and marketing tools.
- Enhances Flexibility:
- Enables advanced tracking setups like e-commerce analytics, custom user actions, and multi-step conversion funnels.
The DataLayer is a pretty unique piece of technical jargon if you’re just getting started with GTM.
But believe me, it can be super powerful once you understand how it works in conjunction with our components and how you can utilize it for your tracking.
Everything is built on the construct of the dataLayer, and if you want to master GTM, you’d better understand how to pull information from it, push information into it, and how it can interact with Tags, Triggers, and Variables.
6. GTM Events
After mastering the Data Layer, it’s essential to understand another critical concept in Google Tag Manager: Events. These represent moments in time when something significant happens on your website or app.
In GTM, Events act as “checkpoints” that you can use to trigger your Tags, update Variables, and control the sequence of your Tag Deployment. Essentially, they allow you to determine when and under what conditions specific actions should occur. For instance:
- A Data Layer Event can trigger a purchase tag when a user completes a transaction.
- It can also update Variables to pass dynamic data (e.g., product IDs or prices) at the right moment.
It’s important to note that GTM Events are not the same as Google Analytics Events.
While Google Analytics Events are a type of data you send to GA (e.g., tracking button clicks), GTM Events are signals or moments within GTM itself that drive your tag logic.
7. HTML / CSS / Javascript
Google Tag Manager is seen as this non-technical solution to a technical problem, but it is a fancy JavaScript injector.
If you want to be efficient in using it, it is necessary to know your HTML, CSS, and Javascript. The foundation of how a Website is built – the more, the better.
If you’re a beginner, then check out freeCodeCamp to get started learning concepts of modern Web Development today.
Or for advanced users, check out our advanced Javascript course.
Enough with all the specifics of Google Tag Manager… let’s talk about some principles that you will learn with experience
8. Advantages / Shortcomings of GTM
Once you understand the technical details of GTM a bit closer, you will realize that JavaScript can’t do everything, and therefore, GTM also has limitations.
As long as you stay in the browser, GTM can help you track all kinds of Interactions, but once you leave the browser, GTM can’t be used as efficiently. Be aware of these shortcomings and adjust your Measurement plan accordingly.
9. Debugging
Every seasoned GTM implementer has run into trouble at some point.
Knowing how to debug your installation and find the root cause can only be learned by understanding the tools of the trade: the Debug console, the JavaScript console, or tools like WASP inspector can reveal what went wrong.
10. Where to Get Help
This last point is a natural one in any learning experience. To reach any kind of mastery, you will need to know what to do when you get stuck. So being able to know where to look for help needs to be second nature.
Summary
So there you have it, the top 10 fundamental Google Tag Manager skills I think you should master.
If you want to take your skills a bit further then check out our MeasureMasters membership, where we have included the best-advanced courses, resources, tools, exercises, and more to make it happen.
If you’re into JavaScript and want to find out how to pull more contextual data from users, check out our handy guide on a relative click variable.
Now, I want to hear from you: Which of these points are you struggling with at the moment or are there any key skills you would add to this list? Let us know in the comments below.
Let me know in the comments below, and I’ll make sure to help you out as best as I can.




Hi Julian
I am not keen on learning Java or html. To be able to have a good positive experience with your clients, is it necessary to know java and html? what if I outsourced this part?
Best,
Harin