Last Modified on November 1, 2024
🚨 Note: All standard Universal Analytics properties will stop processing new hits on July 1, 2023. 360 Universal Analytics properties will stop processing new hits on October 1, 2023. That’s why it is recommended to do the GA4 migration.
Website tracking gathers data about your users and their interactions so that you can customize your digital marketing strategy and maximize conversions.
In this guide, we will show you five Google Analytics tracking techniques that every website should use to get consistent, reliable data.
Intro
Tracking is the most important element of data-driven digital marketing. Good tracking practices collect consistent and reliable data that you can analyze to boost your marketing power.
This guide teaches you five techniques that you should be using in Google Analytics tracking and Google Adwords: traffic sources; website conversions; interactions and events; site searches; and 404 page errors. These techniques are simple and require little to no setup, but neglecting one could cause you to miss out on important data.
A robust tracking approach is the key to digital marketing. This guide will help you take advantage of some of the most important tracking techniques to maximize your marketing and boost your business.
Let’s dive in.
1. Traffic Source Tracking
Traffic source tracking tells you where users were before navigating to your website. This is a pretty reliable indicator for how users found your site, which can help you focus your efforts in the awareness step of your marketing funnel.
Google Analytics takes care of source tracking for you. To access it, click Acquisition in the sidebar menu. Under All Traffic, click on Source/Medium.

Google Analytics tracking is usually pretty good at taking care of this automatically. However, if you’re running an advertising or email campaign without certain customizations, some of your source data could be obscured.
By default, Google Analytics will categorize campaign traffic as (direct) / (none), which suggests that users just miraculously appeared on your page from nowhere. This is problematic in data analysis, especially if you have multiple campaigns that you want to compare.

The solution here is to use UTM parameters. If you’re unfamiliar with UTM parameters, then check out our post UTM Tracking and Google Analytics – The Definitive Guide. But once you have them set up, then you’ll get great tracking data from your campaign traffic.
If you get really good with UTM tracking, you can collect and transfer even more detailed data into other tracking tools, marketing systems, and CRM systems so that you will always know how users enter your website. With just a little bit of UTM configuration, you can dramatically upgrade your source tracking in Google Analytics.
2. Website Conversion Tracking
Website conversion tracking (or Goals with Google Analytics Tracking) is a very basic tracking technique, but a lot of people don’t have it installed. You can check which Goals you have configured in the dropdown button next to Conversions on your traffic source table.
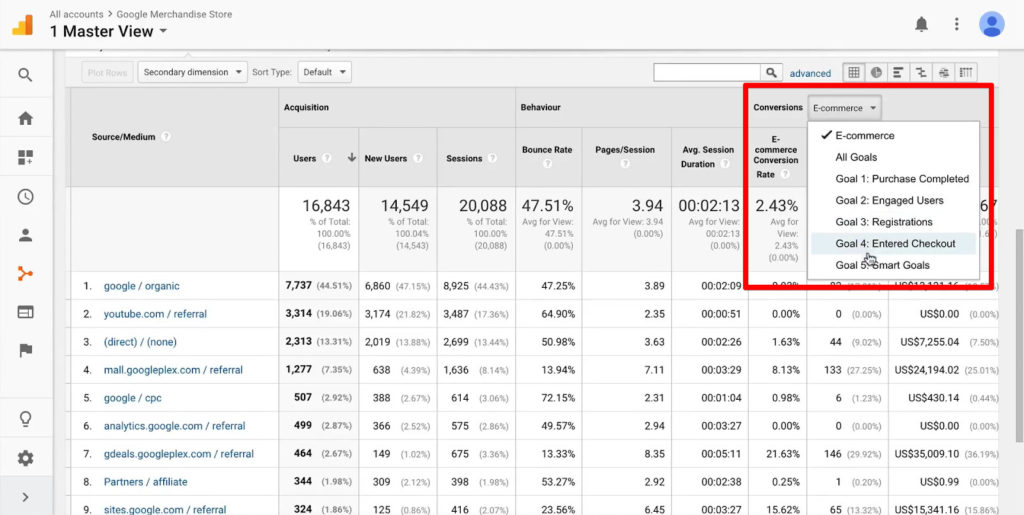
If this dropdown is empty or only has one goal for a homepage visit, you need to spend some time setting up this tracking technique. If you’re unsure how to do this, start with our blog post on Google Analytics 4 conversion tracking.
Goal tracking is essential because Goals define the most important interactions a user takes on your website. That might be a click, submitting a form, or visiting a certain page on your website. Goals signify that the user has reached a certain step in your funnel or has converted.
If it’s important to your business, you need to configure it as a Goal. Make sure that you have this set up in your tracking system so that you can measure interactions that directly determine your business success.
3. Interaction/Event Tracking
Event tracking covers the broad range of potential interactions that a user can take on your website.
By default, Google Analytics tracking and most other tracking tools perform clickstream analysis. This means that they track which pages users visit and in what order. These are recorded as pageviews, which are one simple type of interaction.
Interactions can be more complicated and interesting than just pageviews, though. For example, let’s say that you have an Add to cart button on your website’s shop.

If a user clicks on this button and sees a new page element like this one, then that change counts as an interaction. In fact, any kind of button click, page scrolling, video view, or other user activity can be tracked as an interaction or event.

My favorite tool for event tracking is Google Tag Manager, which I describe in this Google Tag Manager tutorial, check it out if you’re new to event tracking!
There are infinite potential interactions that you could choose to track, but the most efficient configuration will track any and all events related to your funnel. This includes things like scroll tracking, outbound link click tracking, visibility tracking, and more. Anything that could lead to a conversion is important to your analytics and should be tracked.
4. Google Analytics Tracking with Site Search
Site search tracking is a tried-and-true winner for data analytics. This method tracks keywords that users enter in your website’s search box, which generates a wealth of open-ended, organic data.
If you want to collect this type of data, make sure that you have a search box feature enabled on your website! If you didn’t have one already, this is also great for improving user experience and website navigation. You should absolutely take advantage of this feature for tracking.

The search box is incredibly valuable because it tells us what a user is thinking while navigating. This is one of the most organic ways to track a user’s intent when they interact with your site.
If you’ve been working on SEO for a while, you might remember that one of the most popular methods involved Keyword data in Google Analytics tracking. However, Google started encrypting keywords for some users in 2011, then expanded encryption to all users in 2013. Marketers no longer have access to Keyword tracking in Google Analytics as a result.
Despite this, we can still track site searches pretty effectively another way: by tracking Search Terms. To access this tracking data, click Behavior in your sidebar, then under Site Search, click Search Terms.

With this method, you can discover exactly what your users are seeking from your website. This data can help you build pages or offer products to expand your offerings to users. Site search tracking on your website is one of the best ways to research user intent and respond with an improved user experience.
For even more tips and tricks on this tracking method, check out our post How to Setup Site Search in Google Analytics.
5. 404 Page Error Tracking
While we hope that users aren’t seeing a 404 error page very often, we certainly want to know if and when they do. 404 page error tracking can tell you where a user was and what they were trying to do when they encountered this error.
You can see tracking data on 404 error pages by clicking Behavior in the sidebar, then under the Events heading, click Overview. 404 error pages are classified as their own Event Category.

If you click on the 404 error page category, you can get some basic data such as how many unique occurrences were recorded.

If you dig around a little, though, you can get even more specific and useful data. For example, if you click on Event Action, Google Analytics will tell you what type of interaction your user attempted when they encountered the 404 error.

You can also discover where your user was at the time of the 404 error described as a URL. To view this data, click on Event Label.

With 404 error page tracking, you will know when and how these nasty errors come up for users on your website. This information can help you diagnose problems so that you can fix broken pages or elements, thus improving users’ experience. These fixes can save a lot of lost conversions from users giving up when they can’t find what they want.
Want even more tips on 404 error tracking using Google Analytics tracking and Google Tag Manager? Check out our YouTube tutorial here!
Bonus: Visitor Labeling
Want to track your audiences? You should also be tracking visitors that engage in specific interactions on your website, such as logging in or filling out a form. This person is no longer just an ordinary user, but someone who has interacted with your website in a meaningful way.
To do this, click Audience in your sidebar, then select Overview. In this view, you can create audience segments based on actions, conversions, and other user data.

When users visit your website, they interact with your site in the form of logins, button clicks, and pageviews. You can label users according to these interactions, then track specific audiences an even remarket to them.
For instance, you can segment your users into paying customers versus non-paying users, new users versus returning users, and account holders versus unregistered users. In the example below, we have divided up our conversions data based on new users and returning users.

This kind of data makes your work in Google Analytics so much easier. You can segment and filter out users according to your audience targeting, which means you will only look at groups that make sense for your analysis. All of this can be done in Google Analytics, so you don’t have to export and manipulate data elsewhere to get what you want.
You can incorporate Google Tag Manager into this tracking technique to make it even more powerful.
FAQ
How can I track user interactions and events on my website?
Event tracking can be done using tools like Google Tag Manager. By tracking interactions such as button clicks, page scrolling, video views, and other user activities, you can gain insights into user behavior and optimize your marketing efforts.
How can I track 404 page errors in Google Analytics?
To track 404 page errors in Google Analytics, go to the “Behavior” section in the sidebar, then click on “Events” and select “Overview.” 404 error pages are classified as their own Event Category, and you can view specific data such as the type of interaction and the URL where the error occurred.
How can Google Tag Manager enhance visitor labeling?
Google Tag Manager can be used in conjunction with visitor labeling to make the tracking technique more powerful. It enables advanced tracking and customization options for tracking user interactions and behavior on your website.
Summary
There you have it. Traffic sources, website conversions, interactions, site searches, 404 errors, and visitor labels are all invaluable to your Google Analytics tracking toolbox.
Be sure to take advantage of each of these sources to maximize your marketing power!
There are lots of other good tracking techniques depending on your individual tracking goals, but these should be a standard baseline for the vast majority of websites.
Do you have any other Google Analytics tracking techniques that you think should be used for every website? Are there other tracking techniques that you’d like to see explained in a training guide? Let us know in the comments below!